It was a cold winter, the kind that makes you crave warmth, when I first truly understood the enduring appeal of the sauna. For centuries, across cultures, people have turned to heat therapy for its profound benefits, and as we look toward 2025, the science behind these traditions continues to illuminate their value. Regular sauna use isn’t just about relaxation; it’s a powerful tool for health, wellness, and even longevity, offering a holistic approach to well-being that’s both ancient and cutting-edge. Dive in with us to explore how integrating sauna therapy can transform your life.
The Science of Heat: Unlocking Sauna’s Core Physiological Benefits
Stepping into a sauna initiates a cascade of physiological responses within the body, meticulously orchestrated to adapt to the elevated temperatures. This isn’t merely passive warming; it’s a controlled exposure to heat stress that triggers fundamental biological mechanisms, ultimately bolstering resilience and improving systemic function. Understanding these core physiological benefits of sauna provides a robust foundation for appreciating its wider health impacts.
(تصویر پیشنهادی : A cross-section of human skin showing sweat glands actively releasing droplets, with a subtle glow representing heat, symbolizing thermoregulation and the body\’s response to sauna heat. – Physiological response to sauna heat, showing sweat glands and thermoregulation. – sauna-physiology-heat)
Understanding Thermoregulation and Heat Stress Response
When you enter a sauna, your body immediately begins to regulate its internal temperature, a process known as thermoregulation. The rising ambient heat causes your core body temperature to increase by 1-2°C (1.8-3.6°F), similar to a mild fever or intense exercise. This intentional heat stress isn’t harmful; rather, it activates a crucial adaptive response, signaling the body to strengthen its defenses and enhance cellular functions. This physiological “workout” is a key driver behind many of the recognized sauna benefits.
The Role of Mild Hyperthermia in Cellular Adaptation
This controlled increase in body temperature, or mild hyperthermia, acts as a hormetic stressor. It’s a beneficial challenge that pushes cells to become stronger and more efficient. Think of it like a gentle nudge for your body’s internal systems to upgrade themselves, preparing them to better handle future stresses. This adaptation is fundamental to how saunas promote overall resilience.
The Activation of Heat Shock Proteins (HSPs) for Cellular Resilience
One of the most significant cellular responses to sauna heat is the activation and production of Heat Shock Proteins (HSPs). These vital proteins act as molecular chaperones, repairing damaged proteins and preventing cellular dysfunction. They are critical for maintaining protein homeostasis and are strongly linked to cellular longevity and protection against various stressors. Research indicates that regular heat exposure, such as through sauna therapy, can significantly enhance HSP synthesis, contributing to improved cellular health and disease resistance. This protective mechanism is a cornerstone of the health benefits of sauna.
Enhanced Circulation and Blood Flow: A Foundational Benefit
The heat in a sauna causes blood vessels to dilate, leading to a substantial increase in blood flow throughout the body. Your heart rate rises, pumping more blood to the skin’s surface to facilitate cooling through sweating. This enhanced circulation delivers more oxygen and nutrients to tissues while simultaneously aiding in the removal of metabolic waste products. This improved vascular function is not only immediately beneficial for muscle recovery and general vitality but also lays the groundwork for profound cardiovascular advantages. The temporary increase in heart rate to 120–150 bpm effectively mimics moderate physical activity, conditioning your cardiovascular system [heart.org].
Elevating Cardiovascular Health and Longevity Through Sauna Therapy
Regular sauna use is emerging as a powerful tool for promoting cardiovascular health and potentially extending longevity. It’s more than just a pleasant experience; it’s a scientifically validated intervention that mirrors some of the beneficial physiological effects of exercise, particularly on the heart and blood vessels. For those seeking proactive strategies for long-term health, incorporating sauna sessions can be a game-changer.
Sauna and Heart Health: Reducing Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease
The consistent thermal stress from sauna bathing has been shown to positively influence several key risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Studies, including those cited by the American Heart Association, indicate that frequent sauna use can significantly lower the risk of fatal cardiovascular events. It’s a compelling addition to a heart-healthy lifestyle, working synergistically with diet and exercise to protect your most vital organ.
Impact on Blood Pressure and Endothelial Function
One of the most noted sauna benefits for the heart is its effect on blood pressure. Regular sessions can lead to a reduction in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure, particularly in individuals with hypertension. This is partly due to improved endothelial function—the health of the inner lining of your blood vessels—which allows them to dilate and constrict more effectively, promoting healthy blood flow [NCBI PMC5941773]. This improved elasticity is crucial for a well-functioning circulatory system.
Potential for Improved Arterial Stiffness and Vascular Compliance
Beyond blood pressure, sauna use can also help reduce arterial stiffness and improve vascular compliance. Stiff arteries are a hallmark of cardiovascular aging and a predictor of heart disease. By enhancing the flexibility of blood vessels, saunas help maintain a youthful and efficient vascular system, contributing directly to longevity and reducing the burden on the heart.
Mimicking Moderate Exercise: A Cardioprotective Effect
Interestingly, a sauna session can induce a physiological response akin to a moderate-intensity cardiovascular workout. Your heart rate increases, blood vessels dilate, and sweating commences, all without the musculoskeletal strain of physical activity. This “passive exercise” provides a valuable cardioprotective effect, particularly for individuals who may have limitations preventing strenuous physical activity. It helps to condition the heart and improve its efficiency over time.
Exploring the Link Between Regular Sauna Use and Longevity
The cumulative impact of improved cardiovascular health, reduced inflammation, and enhanced cellular resilience directly contributes to an extended healthspan. Research, such as studies published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) and referenced by the NCBI, suggests a compelling link between frequent sauna bathing (4-7 times per week) and a significantly reduced risk of cardiovascular disease mortality, by as much as 50% compared to infrequent users [NCBI PMC5941773]. This points to sauna use as a proactive strategy for longevity, not just short-term wellness.
“Last winter, I began incorporating sauna sessions twice a week into my routine after reading about their cardiovascular and mental health benefits. Initially, stepping into the intense heat was challenging, but after 10 to 15 minutes in a dry sauna, I noticed a profound sense of relaxation and reduced muscle tension. Over the months, my blood pressure readings improved slightly, and I felt less stressed during a particularly demanding work period. The ritual also became a valuable time for mindfulness, allowing me to disconnect from screens and daily anxieties. While I was initially hesitant about dehydration, careful hydration before and after avoided any adverse effects. This experience reinforced how sauna bathing can holistically support wellbeing when practiced responsibly.”
Optimizing Muscle Recovery and Athletic Performance with Sauna
For athletes and fitness enthusiasts, the quest for optimal muscle recovery and enhanced performance is perpetual. Saunas offer a natural, effective method to accelerate this process, moving beyond simple relaxation to actively support the body’s repair mechanisms and improve physical capabilities. Integrating sauna therapy into a post-workout regimen can be a powerful strategy for reaching new personal bests and maintaining peak physical condition.

Accelerating Post-Exercise Recovery: Reducing Muscle Soreness and Fatigue
After a strenuous workout, muscles experience microscopic tears and metabolic waste accumulation, leading to soreness and fatigue. The heat from a sauna significantly enhances blood flow to these fatigued muscles, helping to flush out lactic acid and other metabolic byproducts more efficiently. This improved circulation also delivers fresh oxygen and nutrients essential for repair, making it a stellar tool for post-exercise recovery and reducing Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness (DOMS).
The Role of Heat Exposure in Muscle Repair and Growth
Beyond immediate recovery, regular heat exposure in a sauna can also support long-term muscle repair and even growth. The activation of Heat Shock Proteins (HSPs), as discussed earlier, plays a critical role here by protecting muscle cells from damage and aiding in the proper folding and function of proteins involved in muscle repair. Additionally, some research suggests that heat stress may positively influence growth hormone levels, which are crucial for muscle anabolism.
Enhancing Blood Flow to Muscle Tissues
The deep penetrating heat of a sauna causes significant vasodilation, particularly in the peripheral tissues. This means more blood rushes to your tired muscles, delivering not just oxygen but also vital amino acids and glucose for rebuilding. This targeted increase in blood flow to muscle tissues is a direct mechanism by which saunas accelerate healing and prepare your body for the next challenge.
Supporting Joint Health and Flexibility
The warmth of a sauna has a soothing effect on stiff joints and connective tissues. Increased circulation helps to lubricate joints and reduce inflammation, which can alleviate discomfort and improve overall flexibility. For individuals dealing with mild joint pain or looking to enhance their range of motion, regular sauna sessions can provide significant relief and contribute to sustained physical agility.
Sauna for Mental Well-being: Stress Reduction and Cognitive Clarity
In our fast-paced world, finding moments of peace and clarity is more crucial than ever. The sauna offers a unique sanctuary, providing profound mental well-being benefits that extend far beyond physical warmth. It’s a powerful natural antidote to daily pressures, promoting stress reduction, emotional balance, and even boosting cognitive functions.
(تصویر پیشنهادی : A serene individual meditating or deeply relaxed on a sauna bench, surrounded by soft, warm light, embodying peace, stress relief, and mental clarity. – Person experiencing stress relief and mental clarity in a tranquil sauna setting. – sauna-mental-wellness-relaxation)
Harnessing Endorphins for Mood Elevation and Stress Relief
The heat and the subsequent physiological responses in a sauna stimulate the release of endorphins—the body’s natural “feel-good” hormones. These neurochemicals produce a sense of euphoria, often described as a “sauna high,” which is highly effective in mood elevation and profound stress relief. It’s a natural pathway to alleviate anxiety and improve your overall emotional state, leaving you feeling refreshed and invigorated.
The Relaxation Response: Calming the Nervous System
Beyond endorphins, the tranquil environment of a sauna encourages the body’s relaxation response. The warmth, the quiet, and the absence of external distractions allow the parasympathetic nervous system—responsible for “rest and digest”—to activate. This calms the entire nervous system, reducing the physiological markers of stress such as cortisol levels, leading to a profound sense of inner peace and tranquility. This calming the nervous system is a key aspect of sauna for stress relief.
Enhancing Sleep Quality and Reducing Insomnia
Many individuals struggle with sleep quality and insomnia. Incorporating a sauna session, particularly in the evening, can significantly improve your ability to fall asleep faster and achieve deeper, more restorative sleep. The physiological cooling process that occurs after exiting the hot sauna signals to the body that it’s time to rest, aligning with the natural drop in core body temperature required for sleep initiation. This makes sauna a natural aid in reducing insomnia.
Potential Cognitive Benefits: Focus and Mental Acuity
While the research is still developing, some studies suggest that regular sauna use may offer cognitive benefits. The increased blood flow to the brain, along with the reduction in stress and improved sleep, can contribute to enhanced focus, clearer thinking, and improved mental acuity. It’s believed that the mild heat stress and the release of neurotrophic factors might play a role in supporting brain health and function.
Detoxification and Skin Health: A Deeper Clean
Beyond the visible steam and comforting heat, a sauna session provides a powerful internal cleanse that significantly impacts both detoxification and skin health. It’s not just about feeling clean; it’s about a deeper, physiological purification that revitalizes your largest organ. For those seeking a natural approach to a healthier complexion and systemic cleansing, the sauna offers an undeniable pathway.

The Mechanism of Sweating: Eliminating Toxins and Heavy Metals
One of the most well-known sauna benefits is the copious sweating it induces. Sweating is your body’s natural mechanism for cooling, but it also serves as a potent pathway for detoxification. Scientific studies suggest that sweat can contain trace amounts of certain heavy metals (like lead, mercury, cadmium, and arsenic) and other environmental toxins, helping to offload the burden on your kidneys and liver [CDC heat stress guidelines]. It’s a natural, efficient way for your body to purge unwanted substances.
Improving Skin Tone and Complexion through Increased Circulation
The surge in blood flow to the skin during a sauna session delivers a fresh supply of oxygen and nutrients to the epidermal cells. This increased circulation not only gives the skin a healthy, vibrant glow but also supports the repair and regeneration of skin cells. Regular use can lead to improved skin tone and a more radiant complexion, making your skin look and feel healthier from the inside out.
Addressing Certain Skin Conditions: Benefits of Sauna for Dermatological Health
While not a cure, sauna use can offer symptomatic relief and support for certain skin conditions. The deep cleansing action of sweating can help clear pores, which may benefit individuals prone to acne. For those with dry skin, the increased moisture in traditional saunas and the improved circulation can enhance hydration. However, individuals with specific dermatological conditions like rosacea or eczema should consult a dermatologist before regular use, as heat can sometimes exacerbate certain sensitivities.
Navigating Sauna Types: Traditional vs. Infrared Therapy
When considering integrating sauna therapy into your wellness routine, you’ll inevitably encounter two primary types: traditional saunas and infrared saunas. While both offer significant health benefits, they achieve their effects through different mechanisms and provide distinct experiences. Understanding these differences is key to choosing the right sauna type for your personal wellness goals.
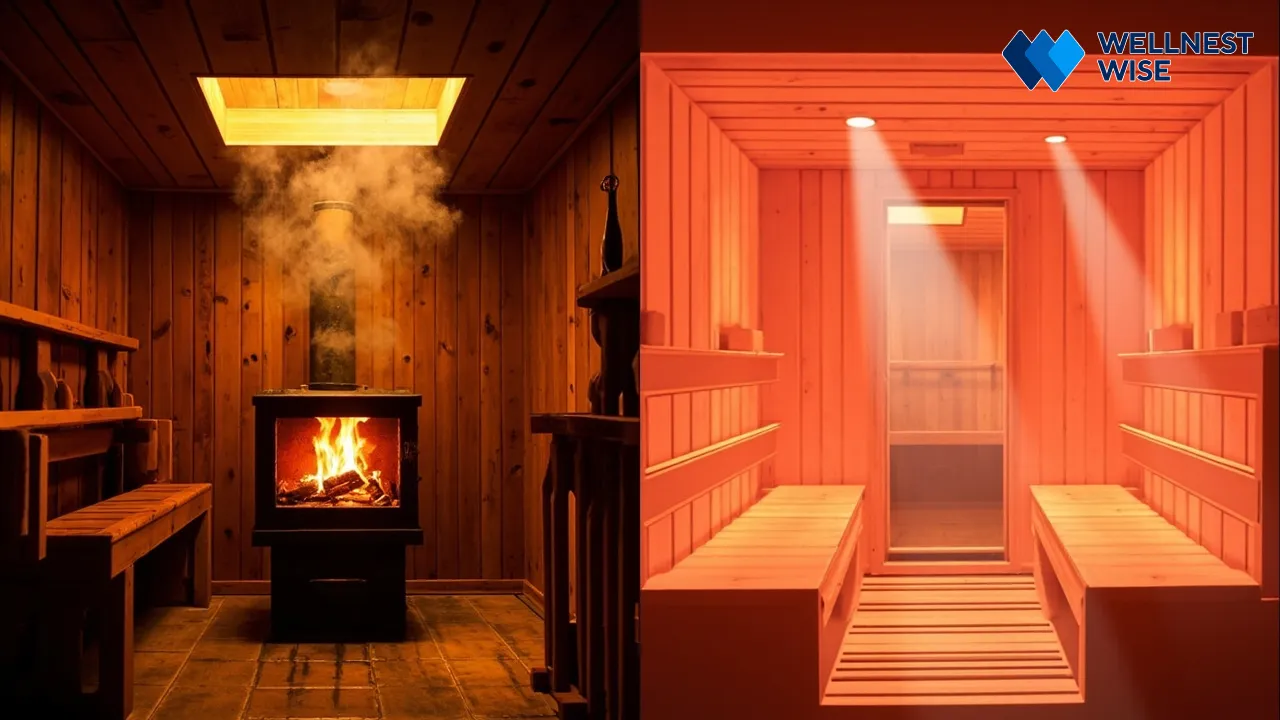

Traditional Saunas: Finnish Heat and Steam
Traditional saunas, often referred to as Finnish saunas, operate at high air temperatures, typically ranging from 70-100°C (158-212°F). The heat is generated by an electric or wood-fired stove that heats rocks, over which water can be poured to create steam (known as löyly). This combination of intense dry heat and adjustable humidity creates a profoundly enveloping warmth that promotes profuse sweating and a deep sense of cleansing.
The Experience and Physiological Impact of High Heat and Humidity
The experience in a traditional sauna is one of intense heat that warms the air around you, leading to vigorous sweating. The added steam can open airways, making it feel beneficial for respiratory passages. The physiological impact includes a rapid increase in core body temperature, significant cardiovascular load, and a robust thermoregulation response, aligning with many of the core sauna benefits discussed earlier. Sessions typically last between 10-20 minutes.
Infrared Saunas: Deeper Penetration with Lower Ambient Temperatures
Infrared saunas operate at significantly lower ambient air temperatures, usually between 45-60°C (113-140°F). Instead of heating the air, infrared heaters emit light waves (infrared radiation) that directly penetrate the body’s tissues, warming you from the inside out. This allows for a deeper therapeutic heat penetration at a more tolerable air temperature, making it a comfortable option for those sensitive to the extreme heat of traditional saunas.
Exploring Near, Mid, and Far Infrared Spectrum Benefits
Infrared saunas often utilize different wavelengths of infrared light:
- Near-Infrared (NIR): Often used for skin rejuvenation, wound healing, and cellular regeneration.
- Mid-Infrared (MIR): Targets soft tissue, muscle relaxation, and pain relief.
- Far-Infrared (FIR): The most common type, known for deep tissue detoxification, cardiovascular benefits, and overall relaxation. This broad spectrum of direct heat penetration is a key differentiator of infrared sauna benefits.
Choosing the Right Sauna for Your Wellness Goals
- Traditional (Finnish/Steam) Sauna: Ideal for those who enjoy intense heat (70-100°C / 158-212°F), high humidity from steam over hot rocks, intense sweating, and respiratory benefits. Sessions are typically shorter due to the high heat.
- Infrared Sauna: Best for individuals seeking deeper heat penetration into the body at lower air temperatures (45-60°C / 113-140°F). Different infrared wavelengths (near, mid, far) offer specific benefits for skin, pain relief, and detoxification. It’s often more suitable for those sensitive to high heat or seeking longer, milder sessions.
- Combination Saunas: Some modern saunas offer both traditional and infrared heating options, providing the versatility to switch between experiences based on your preference or specific wellness goals.
- Health Considerations: If you have specific health conditions or heat sensitivities, an infrared sauna with its lower ambient temperature might be more suitable. Always consult a healthcare professional to determine the best sauna type for your individual needs.
Safe Sauna Practices and Important Precautions for Optimal Health
While the health benefits of sauna are extensive, practicing safe sauna use is paramount to maximizing these advantages and preventing any adverse effects. Just like any powerful wellness tool, knowing how to use it correctly, understanding your body’s signals, and recognizing potential contraindications are crucial for an enjoyable and genuinely beneficial experience. Prioritizing sauna safety ensures you reap the rewards without unnecessary risks.

Essential Hydration: Before, During, and After Your Sauna Session
Sweating is a primary mechanism by which saunas deliver many of their benefits, but it also means significant fluid loss. Therefore, essential hydration is non-negotiable. Begin hydrating well before your session, drink water during if tolerated (especially in longer sessions or if you feel thirsty), and replenish fluids generously after exiting the sauna. Electrolyte-rich beverages can also be beneficial, particularly after longer or more frequent sessions, to replace lost minerals.
Optimal Session Duration and Frequency for Wellness Benefits
There’s no one-size-fits-all rule for optimal session duration and frequency, as it depends on your individual tolerance, health status, and the type of sauna. Generally, sessions in traditional saunas range from 10-20 minutes, while infrared saunas, with their lower temperatures, might allow for 20-45 minute sessions. For wellness benefits, 2-4 sessions per week are often recommended, but even 1-2 sessions can provide significant advantages. Always start slow, listen to your body, and gradually increase duration as you adapt.
Understanding Your Body’s Signals: When to Exit the Sauna
Your body will send clear signals when it’s had enough heat. It’s crucial to pay attention to these. Signs that you should immediately exit the sauna include:
- Feeling dizzy or lightheaded
- Nausea
- Extreme discomfort or agitation
- Headache
- Any sensation of severe overheating or weakness
Never push yourself beyond your comfort level. The goal is relaxation and benefit, not endurance.
Key Safety Precautions and Contraindications for Sauna Use
| Condition/Factor | Precaution/Recommendation | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| :————— | :———————————————————- | :——————————————————————————- |
| Cardiovascular Issues | Consult a physician, especially with unstable angina, recent heart attack, or severe aortic stenosis. Avoid if advised. | Heat places stress on the cardiovascular system; professional guidance is crucial. |
| Pregnancy | Generally not recommended, especially in the first trimester. Consult an obstetrician. | Potential risks to fetal development and overheating for the mother. |
| Alcohol/Drug Use | Avoid sauna use under the influence of alcohol or recreational drugs. | Impaired judgment, increased risk of dehydration, and cardiovascular strain. |
| Dehydration | Ensure adequate hydration before entering the sauna. | Saunas induce significant fluid loss; pre-existing dehydration can be dangerous. |
| Fever/Illness | Avoid sauna use during acute illness, fever, or infection. | Can exacerbate symptoms, worsen dehydration, and spread illness. |
| Medications | Consult a doctor if taking medications that affect thermoregulation, blood pressure, or cause drowsiness. | Some medications can alter the body’s response to heat. |
| Children/Elderly | Supervised, shorter sessions at lower temperatures are recommended. | Children and elderly may have reduced ability to regulate body temperature. |
| Open Wounds/Infections | Avoid to prevent infection or discomfort. | Heat and moisture can worsen certain skin conditions. |
| Overheating Signs | Immediately exit if experiencing dizziness, nausea, headache, or extreme discomfort. | Indicates the body is struggling to cope with heat; a sign to stop. |
Integrating Sauna into Your Modern Wellness Routine for 2025 and Beyond
In an era where personalized wellness is taking center stage, intelligently integrating sauna therapy into your daily or weekly rhythm is a forward-thinking approach to modern wellness. It’s about more than just sporadic visits; it’s about creating a consistent, adaptable protocol that complements your lifestyle and amplifies your existing health efforts. Let’s explore how to make the sauna benefits a sustainable part of your journey for 2025 and beyond.

Developing a Personalized Sauna Protocol
A truly effective wellness routine is one that’s tailored to you. When it comes to sauna use, consider your schedule, tolerance, and specific goals. Are you aiming for muscle recovery after workouts, stress relief after a long day, or cardiovascular conditioning? Start with shorter sessions a couple of times a week and gradually experiment to find what feels best and delivers the most profound sauna benefits for your individual needs.
Timing Your Sessions: Morning Boost or Evening Relaxation
The best time for sauna use often depends on your desired outcome. A morning session can act as an invigorating morning boost, kickstarting your circulation and mental clarity for the day ahead. Conversely, an evening session is often prized for its profound relaxation effects, helping to unwind, reduce stress, and prepare the body for a deeper, more restorative sleep. Experiment with both to see which aligns best with your lifestyle and goals.
Complementary Wellness Practices: Cold Plunge and Mindfulness
The sauna experience can be significantly enhanced when combined with other complementary wellness practices. Alternating between hot (sauna) and cold (e.g., a cold plunge or cold shower) therapies, often called “contrast therapy,” can further boost circulation, reduce inflammation, and enhance the body’s adaptive responses. Additionally, utilizing your sauna time for mindfulness or meditation, disconnecting from devices, can deepen the mental well-being benefits, transforming a simple heat session into a profound meditative retreat.
Sustaining Long-Term Benefits: Consistency and Adaptability
The key to unlocking the full spectrum of sauna benefits lies in consistency and adaptability. Regular, even if infrequent, use will yield far greater results than intense but sporadic sessions. Be flexible with your routine; life happens. If you miss a session, simply get back to it when you can. The goal is to make sauna therapy a sustainable and enjoyable component of your overall wellness journey, evolving with your needs over time to support long-term health.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Health with Sauna Benefits
As we navigate the complexities of modern life, the timeless practice of sauna bathing stands out as a powerful, scientifically validated tool for enhancing health, wellness, and longevity. From bolstering cardiovascular health and accelerating muscle recovery to profoundly reducing stress and promoting deeper detoxification, the sauna benefits are holistic and far-reaching. It’s a remarkable synthesis of ancient wisdom and cutting-edge science, perfectly aligned with the evolving demands of 2025 wellness.

The Holistic Impact of Regular Sauna Use on Modern Health
The true strength of regular sauna use lies in its holistic impact. It’s not just addressing one aspect of health but orchestrating a symphony of positive physiological changes across multiple bodily systems. By stimulating Heat Shock Proteins, improving circulation, calming the nervous system, and aiding in detoxification, saunas help create a more resilient, balanced, and vibrant you. It’s an investment in your physical and mental capital, yielding dividends for years to come.
Empowering Your Wellness Journey with Evidence-Based Practices
Ultimately, incorporating sauna therapy into your lifestyle is about empowering your wellness journey with evidence-based practices. Armed with the knowledge of its profound health benefits and best practices for safe use, you can confidently integrate this ancient tradition into your modern routine. Start small, listen to your body, and allow the warmth to guide you toward a healthier, more relaxed, and longer life. Your journey to optimal well-being for 2025 and beyond awaits.
FAQ
Practical, scientific Q&A
What are the most significant health benefits of using a sauna regularly?
Regular sauna use offers significant benefits for cardiovascular health (reducing risk of heart disease, lowering blood pressure), enhances muscle recovery and reduces soreness, promotes stress relief and improves mood through endorphin release, aids in detoxification via sweating, and supports skin health by improving circulation and cleansing pores.
How frequently should one use a sauna to achieve optimal wellness results?
For optimal wellness results and to significantly reduce risks of cardiovascular disease, research suggests using a sauna 4-7 times per week. However, even 2-3 sessions per week can yield substantial health benefits. The key is consistency, starting with shorter durations (10-20 minutes) and gradually increasing as your body adapts.
Are there any specific risks or contraindications for sauna use that I should be aware of?
Yes, sauna use comes with important precautions. Individuals with unstable cardiovascular conditions, those who are pregnant, or anyone under the influence of alcohol or drugs should avoid saunas. It’s crucial to stay well-hydrated before and after sessions and to immediately exit if you experience dizziness, nausea, or extreme discomfort. Always consult a physician if you have pre-existing health conditions or are on medication.














